Godet Columbus (DIN 15232)
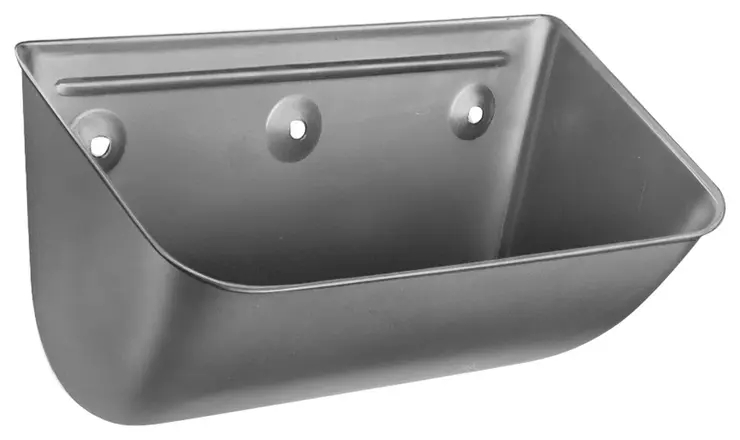
Godet d'élévateur Type G
G80, G90, G100, G110, G120, G130, G150, G160/1.5, G160/2.0, G180/1.5, G180/2.0, G200/1.5, G200/2.0, G225/1.5. G225/2.0, G250/1.5, G250/2.0, G300/1.5, G300/2.0, G350/1.5, G350/2.0, G400/2.0, G400/2.5, G500, GS350-230, GS350-240, GS500/1 HDP, GS500HDP
Godet d'élévateur de fabrication emboutie, adapté à la manutention de produits s’écoulant librement dans des élévateurs à vitesse moyenne.

Product Features
- Fabrication emboutie
- Godet d'élévateur adapté à la manutention des produits s'écoulant librement sur des élévateurs à vitesse moyenne
- Fourni avec des trous de fixation emboutis standard
Material
Inox,
Acier
Use by Industry
Agriculture
Use by Product
Céréales,
Pellets & Produits légers,
Industrie légère
Specifications

| | G-TYPE - Columbus | A | B | C | D* | T | Weight | Capacity | Capacity | Holes | E | F | G | ||||
| STANDARD RANGE | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (kg) | Z2 (total) | Z3 (water) | No. | (Ø mm) | (mm) | (mm) | |||||
| G80 | 80 | 75 | 80 | 40 | 1.0 | 0.13 | 0.25 | 0.16 | 2 | 8.0 | 43 | 19 | |||||
| G90 | 90 | 80 | 85 | 45 | 1.0 | 0.16 | 0.33 | 0.22 | 2 | 8.0 | 46 | 19 | |||||
| G100 | 100 | 90 | 91 | 48 | 1.0 | 0.18 | 0.42 | 0.27 | 2 | 8.0 | 58 | 23 | |||||
| G110 | 110 | 95 | 95 | 50 | 1.0 | 0.21 | 0.51 | 0.33 | 2 | 8.0 | 64 | 26 | |||||
| G120 | 120 | 100 | 105 | 55 | 1.0 | 0.25 | 0.70 | 0.41 | 2 | 8.0 | 67 | 29 | |||||
| G130 | 130 | 105 | 110 | 58 | 1.0 | 0.30 | 0.81 | 0.49 | 2 | 8.0 | 78 | 32 | |||||
| G140 | 140 | 115 | 117 | 63 | 1.0 | 0.33 | 1.05 | 0.62 | 2 | 8.0 | 86 | 35 | |||||
| G150 | 150 | 125 | 123 | 66 | 1.0 | 0.36 | 1.21 | 0.75 | 2 | 8.0 | 87 | 33 | |||||
| G160/1.5 | 160 | 125 | 126 | 70 | 1.5 | 0.57 | 1.31 | 0.89 | 2 | 9.5 | 101 | 36 | |||||
| G160/2.0 | 160 | 125 | 126 | 70 | 2.0 | 0.76 | 1.31 | 0.89 | 2 | 9.5 | 101 | 35 | |||||
| G180/1.5 | 180 | 130 | 130 | 76 | 1.5 | 0.67 | 1.62 | 1.04 | 2 | 9.5 | 110 | 39 | |||||
| G180/2.0 | 180 | 130 | 130 | 76 | 2.0 | 0.89 | 1.62 | 1.04 | 2 | 9.5 | 110 | 39 | |||||
| G200/1.5 | 200 | 140 | 145 | 88 | 1.5 | 0.84 | 2.25 | 1.50 | 2 | 9.5 | 131 | 45 | |||||
| G200/2.0 | 200 | 140 | 145 | 88 | 2.0 | 1.12 | 2.25 | 1.50 | 2 | 9.5 | 131 | 45 | |||||
| G225/1.5 | 225 | 145 | 153 | 90 | 1.5 | 1.01 | 2.81 | 1.80 | 3 | 9.5 | 70 | 40 | |||||
| G225/2.0 | 225 | 145 | 153 | 90 | 2.0 | 1.30 | 2.81 | 1.80 | 3 | 9.5 | 70 | 40 | |||||
| G250/1.5 | 250 | 150 | 158 | 92 | 1.5 | 1.13 | 3.15 | 2.07 | 3 | 9.5 | 77 | 45 | |||||
| G250/2.0 | 250 | 150 | 158 | 92 | 2.0 | 1.46 | 3.15 | 2.07 | 3 | 9.5 | 77 | 45 | |||||
| G300/1.5 | 300 | 155 | 160 | 95 | 1.5 | 1.35 | 4.20 | 2.75 | 3 | 9.5 | 104 | 48 | |||||
| G300/2.0 | 300 | 155 | 160 | 95 | 2.0 | 1.74 | 4.20 | 2.75 | 3 | 9.5 | 104 | 48 | |||||
| G350/1.5 | 350 | 180 | 190 | 100 | 1.5 | 1.86 | 6.37 | 4.03 | 4 | 11.0 | 90 | 54 | |||||
| G350/2.0 | 350 | 180 | 190 | 100 | 2.0 | 2.35 | 6.37 | 4.03 | 4 | 11.0 | 90 | 54 | |||||
| G400/2.0 | 400 | 200 | 212 | 112 | 2.0 | 3.00 | 8.17 | 5.32 | 4 | 11.0 | 100 | 80 | |||||
| G400/2.5 | 400 | 200 | 212 | 112 | 2.5 | 3.75 | 8.17 | 5.32 | 4 | 11.0 | 100 | 80 | |||||
| G500 | 500 | 224 | 236 | 125 | 3.0 | 6.00 | 14.50 | 9.50 | 5 | 14.0 | 100 | 90 | |||||
| G-TYPE - Columbus | A | B | C | D* | T | Weight | Capacity | Capacity | Holes | E | F | G | |||||
| SPECIAL RANGE | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (kg) | Z2 (total) | Z3 (water) | No. | (dia mm) | (mm) | (mm) | |||||
| GS350-230 | 359 | 232 | 236 | 108 | 2.5 | 3.85 | 9.97 | 5.22 | 4 | 12.0 | 80 | 90 | |||||
| GS350-240 | 359 | 244 | 236 | 125 | 2.5 | 3.91 | 10.25 | 6.80 | 4 | 12.0 | 80 | 90 | |||||
| GS500/1 HDP | 500 | 226 | 247 | 117 | 9.0 | 2.35 | 13.35 | 6.90 | |||||||||
| GS500HDP | 500 | 240 | 253 | 117 | 8.5 | 2.44 | 14.58 | 7.98 | |||||||||
* Note: les dimensions sont intérieures selon norme DIN.